What Kinds of Cryptocurrencies to Choose for Development and More Adoption
Launching a cryptocurrency only matters if people actually use it. Many projects fail not because of poor development, but because the type of cryptocurrency they choose does not fit real user needs.
Some currencies are created for payments, others for long-term holding, platform access, or protocol governance. Each type fits different use cases and influences adoption through distinct user behaviors. When the purpose is unclear, user engagement declines rapidly.
This article explains the main types of cryptocurrencies suitable for development today and focuses on which ones are more likely to gain real adoption. The goal is to help you choose a cryptocurrency model that users understand, trust, and continue to use.
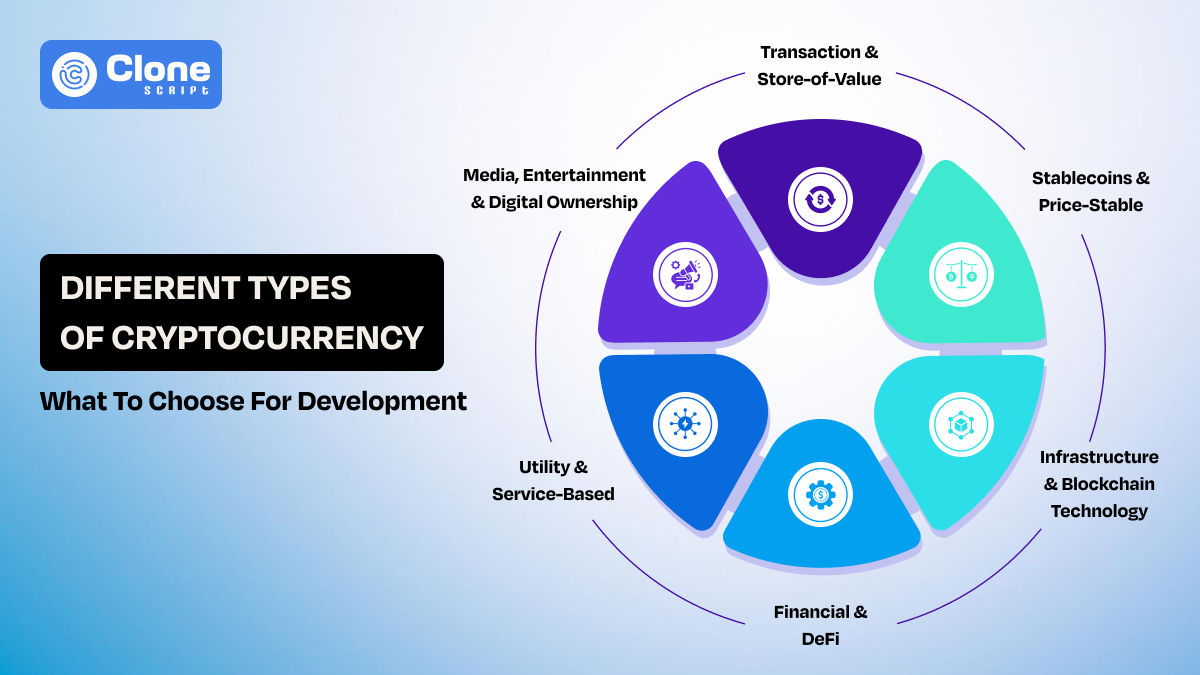
What Are the Different Types of Cryptocurrency Development?
Cryptocurrency development is not a single process with one outcome. The type of crypto you choose defines how users interact with it, how value moves through the system, and how adoption grows over time.
Each cryptocurrency is built around a primary function. Some focus on transferring value. Others exist to secure networks, enable applications, or provide access to digital services. When these functions are mixed without purpose, users struggle to understand the product.
Cryptocurrencies can be grouped into functional categories based on:
-
How users use the token
-
Where value is created
-
What drives repeat usage
-
How trust is established
The sections that follow break down these categories and explain how each type influences adoption with real-world usage instead of assumptions.
1. Transaction & Store-of-Value Cryptocurrencies
These cryptocurrencies are commonly associated with the concept of “digital money.” The purpose is simple: preserve value or transfer it between parties. Because the purpose is familiar, these cryptocurrencies often achieve early adoption as long as their role is clearly defined.

Clarity of purpose matters most in this category. A cryptocurrency built for daily payments behaves very differently from one designed for long-term holding.
-
Payment Cryptocurrencies
Payment cryptocurrencies are created for regular, repeat transactions. Users expect them to be fast, affordable, and simple to use. The moment a payment token feels slow or expensive, adoption stalls.
These crypto tokens prioritize the following things:
-
Fast transaction confirmation within a few seconds without any intermediaries.
-
Low and predictable fees compared to traditional fiat payment systems.
-
Strong wallet and exchange support make payments easy to manage and widely accessible.
-
Straightforward onboarding helps users adopt the currency regardless of technical expertise.
Examples of payment cryptocurrencies include:
-
Bitcoin (used globally for peer-to-peer transfers)
-
Litecoin (optimized for faster transactions)
-
Bitcoin Cash (focused on low-fee payments)
These examples show that adoption grows when sending value feels intuitive and reliable.
Best suited for:
These digital currencies are well-suited for retail payments, cross-border remittances, freelancer payouts, and everyday digital transactions.
-
Store-of-Value Cryptocurrencies
Store-of-value crypto tokens are designed to be held rather than spent. Users adopt them as long-term assets, with the expectation that supply rules will remain stable over time.
When creating these cryptocurrencies, the development priorities should include:
-
A limited or predictable token supply that supports long-term value preservation.
-
High network security is essential to prevent manipulation and protect supply integrity.
-
Minimal changes to core protocol rules help maintain long-term investor trust.
-
Resistance to manipulation strengthens investor confidence and long-term value growth.
Common examples include:
-
Bitcoin (widely treated as a long-term holding asset along with crypto payments)
-
Wrapped Bitcoin (used as a value store within DeFi ecosystems)
Trust is the prime element that drives adoption in this category. Once users believe the rules are stable, they are more willing to commit capital for the long term.
Best suited for:
Projects targeting long-term holders, institutional interest, or value preservation use cases can depend on these cryptocurrencies.
-
Memecoins
Famous meme coins gain adoption through culture, humor, and community participation rather than technical features. Their simplicity lowers the barrier to entry, which explains their rapid spread. Visibility from public figures often accelerates awareness and early adoption.
Early-stage memecoins usually focus on the following:
-
Easy token access can onboard new investors who want a short-term profit benefit.
-
A strong social presence helps attract liquidity and early community support. Managing the meme community is an important task to get more attention towards the project.
-
Community-led promotion and marketing for meme coins reflects decentralized participation, often coordinated through DAOs.
However, memecoins that maintain acceptance over time add structure and purpose to owning cryptocurrencies.
Well-known examples include:
-
Dogecoin (community-driven with simple payment use cases)
-
Shiba Inu (expanded into staking, NFTs, and ecosystem tools)
These examples show that memecoins can evolve into broader platforms when community energy is supported by real utility.
Best suited for:
Projects where community engagement, participation, and brand identity play a central role in crypto adoption can depend on these digital currencies.
2. Stablecoins & Price-Stable Cryptocurrencies
Stablecoins exist to solve one of the biggest barriers to cryptocurrency adoption: price volatility. For many users, especially businesses, unpredictable value makes everyday use impractical. Stablecoins remove that friction by keeping prices relatively fixed.

Adoption of stablecoins is driven by trust, transparency, and operational reliability. Below are the main stablecoin models used in cryptocurrency development today.
-
Fiat-Backed Stablecoins
Fiat-backed stablecoins are tied to traditional currencies such as the US dollar or the Euro. Their value comes from real-world reserves, not market speculation like crypto does.
This cryptocurrency model focuses on the following elements in development:
-
Transparent reserve management is a key to maintaining trust in the cryptocurrency.
-
Reliable minting and redemption mechanisms reinforce confidence in price stability.
-
Regular audits and transparent reporting are especially important for newly launched fiat-backed stablecoins.
-
Strong compliance controls aligned with regional regulations support long-term adoption.
Common examples include:
-
USDT (Tether) is widely used for trading and transfers.
-
USDC is known for regulatory alignment and transparency.
-
BUSD (historically used within exchange ecosystems).
These stablecoins see strong adoption because users understand exactly what one token represents.
Best suited for:
Crypto trading platforms, payment systems, payroll solutions, and enterprise blockchain applications use stablecoins.
-
Crypto-Collateralized Stablecoins
Crypto-collateralized stablecoins are backed by other currencies instead of fiat reserves. They depend on smart contracts and over-collateralization to maintain stability rather than volatility.
In this type of decentralized currency development, prioritize the following:
-
Automated collateral management that helps maintain price stability.
-
Liquidation mechanisms protect protocol solvency by rebalancing collateral and outstanding debt during market volatility.
-
Accurate price oracle integration ensures reliable collateral valuation.
-
Governance-based risk control removes the worries about the loss of assets.
Well-known examples include:
-
DAI, backed by multiple crypto assets and governed by a DAO
This model appeals to users who value decentralization and understand crypto market mechanics.
Best suited for:
DeFi platforms and users who prefer trustless financial systems for their needs use these cryptocurrencies.
-
Algorithmic Stablecoins
Algorithmic stablecoins attempt to maintain price stability through supply and demand logic, rather than direct collateral. These systems adjust token supply based on market conditions, using incentives to influence behavior.
Notable examples include:
-
FRAX (a partially algorithmic model)
Adoption depends heavily on confidence in the underlying economic design. If confidence weakens, adoption and usage can decline.
Best suited for:
These currencies can be useful to advanced teams that are experimenting with economic models and controlled market environments.
3. Infrastructure & Blockchain Technology Cryptocurrencies
Infrastructure-focused Web3 digital currencies are rarely adopted for emotional or speculative reasons. They are selected because other products depend on them. Their success is measured by how many applications, networks, or systems depend on them in the background.

When developers build on an infrastructure layer, users follow through the applications they use.
-
Application Platform Cryptocurrencies
This type of cryptocurrency is designed to work with blockchains. It allows developers to deploy smart contracts and decentralized applications. Their adoption begins with developers, not end users, as payment currencies and stablecoins do.
The development priorities should include:
-
Stable smart contract execution with an encrypted nature that keeps things organized and trustworthy.
-
Clear development tools and well-documented frameworks encourage wider developer adoption.
-
Predictable network fees help developers and users understand transaction costs in advance.
-
Scalable infrastructure is important to have and manage the adoption without facing downtime.
Prominent examples include:
-
Ethereum is the most widely used smart contract platform.
-
Solana is focused on high throughput and low fees.
-
Avalanche is designed for fast finality and customizable networks.
These platforms gain adoption when developers continue to build and maintain crypto applications on them.
Best suited for:
Projects aiming to create developer ecosystems, decentralized platforms, or multi-application networks can use these cryptocurrencies.
-
Scaling & Layer-2 Cryptocurrencies
Layer-2 cryptocurrencies are made to improve the user experience on existing blockchains. Users adopt them because they reduce costs and speed up transactions. It can be done without changing how users interact with applications.
This cryptocurrency development focuses on:
-
Transaction batching and compression maintain the transparency in the networks and remove congestion.
-
Seamless integration with base layers provides a smooth interactivity from one chain to another.
-
Security alignment with base networks reduces vulnerabilities and preserves user trust.
Well-known examples include:
-
Polygon is widely used for scaling Ethereum applications.
-
Arbitrum and Optimism are focused on rollup-based scaling.
Adoption for these currencies grows when users feel the benefits without needing to understand the technical details.
Best suited for:
Applications facing high fees or congestion on main blockchains can depend on these cryptocurrencies.
-
Oracle, Bridge & Communication Tokens
These currencies allow data transfer and interoperability between blockchains and external systems. While users may never interact with these tokens directly, entire ecosystems depend on them.
In this type of digital assets development, the challenges are:
-
Data accuracy and reliability are a main concern because two or more blockchains operate together. So, maintaining data consistency is needed.
-
Cross-chain security is another important thing to notice. Every chain is secured, but their use cases are different, so keeping them organized needs expertise.
-
Effective network coordination makes easy cross-chain interaction while maintaining security.
Recognized examples include:
-
Chainlink is widely used for decentralized price feeds.
-
Polkadot enables cross-chain communication.
-
Cosmos is focused on blockchain interoperability.
Dependency encourages adoption in these cryptocurrencies. Web3 applications depend on these systems; the usage is structural rather than optional.
Best suited for:
Multi-chain ecosystems, data-driven smart contracts, and interoperable blockchain networks can use these cryptocurrencies.
4. Financial & DeFi Cryptocurrencies
Financial and DeFi cryptocurrencies are replacing or simplifying traditional financial functions. Instead of banks, brokers, or payment processors, these tokens enable users to borrow, lend, trade, or earn yields directly on blockchain networks.

-
DeFi Protocol Tokens
DeFi protocol tokens help decentralized financial platforms that offer services similar to banks, exchanges, and investment products. Here, no centralized control exists.
These digital currencies are adopted because they give users:
-
Direct access to financial services without traditionally relying on banks or brokers.
-
Control over assets, as users retain custody through self-managed wallets.
-
Automated execution, where smart contracts replace manual processing.
The development focus includes:
-
Smart contracts must be secure and thoroughly audited to prevent fund loss.
-
Liquidity mechanisms are required for smooth trading and lending.
-
Governance models that allow token holders to influence protocol changes.
Prominent examples include:
-
Uniswap is a decentralized exchange for token swapping.
-
Aave is a lending and borrowing protocol.
-
MakerDAO, which manages decentralized stablecoin issuance.
Adoption grows because users gain faster access to capital with fewer restrictions than traditional finance.
Best suited for:
Projects including decentralized crypto exchanges development, lending platforms, yield-generation products, or governance-driven financial systems use these cryptocurrencies.
-
Asset-Backed Cryptocurrencies
Asset-backed cryptocurrencies represent real-world or digital assets on the blockchain. They create a bridge between traditional asset value and decentralized systems.
Users adopt these cryptocurrencies because they:
-
Provide tangible backing that reduces volatility compared to purely speculative assets.
-
Enable accurate ownership of high-value assets like real-world, luxurious fixed assets.
-
Improve liquidity for assets that are traditionally hard to trade and manage with simplicity.
Development priorities for these cryptocurrencies include:
-
Reliable asset custody and verification on a secure blockchain network.
-
Transparent proof-of-reserve mechanisms with the smart contract deployment.
-
Regulatory awareness to support long-term adoption of the cryptocurrency value.
Well-known examples include:
-
Tokenized gold assets such as Pax Gold
-
Real-estate-backed tokens
-
Commodity-backed digital assets
These cryptocurrencies gain attention when users trust the underlying asset and the system verifying its value.
Best suited for:
This cryptocurrency can be helpful to platforms focused on asset tokenization, stable-value products, or bridging traditional finance with blockchain infrastructure.
5. Utility Tokens & Service-Based Cryptocurrencies
These cryptocurrencies are created to enable specific actions within a digital ecosystem. Their value does not come from speculation alone, but from how effectively they support real use cases inside platforms, applications, or networks.

Users choose utility and service cryptocurrencies because they unlock functionality, reduce frustration, or provide access to services they already want to use.
-
Utility Tokens
These tokens are designed to grant users access to features, products, or services within a blockchain-based platform. They function as digital access keys rather than traditional currencies like BTC and ETH.
Users adopt utility tokens because they:
-
Enable platform usage, such as paying fees or unlocking features, without any intermediaries.
-
Create incentives, rewarding users for participation or contribution in a consistent way.
-
Support ecosystem growth, encouraging long-term engagement and acceptance of the token.
Development should focus on the following areas:
-
Clear token use cases connect directly to platform activity without confusion.
-
Controlled token supply to prevent overinflation and protect user confidence.
-
Easy integration with user workflows keeps these tokens useful.
Prominent examples include:
-
Binance Coin (BNB) is used for transaction fees and ecosystem services.
-
Basic Attention Token (BAT) rewards users and publishers in digital advertising.
-
Filecoin (FIL) is used to pay for decentralized storage services.
Utility tokens gain adoption when users see immediate, practical value rather than speculative benefits.
Best suited for:
Platforms offering SaaS-like services, decentralized applications, marketplaces, or subscription-based blockchain products can depend on the utility cryptocurrency.
-
Service Cryptocurrencies
Service cryptocurrencies facilitate ongoing digital services such as storage, computing power, bandwidth, or content delivery. They operate as payment and coordination mechanisms inside service-based networks.
Users choose these service digital currencies because they:
-
Pay only for what they use, so users can reduce upfront costs.
-
Access decentralized services and avoid vendor lock-in to gain experience with the service.
-
Participate in shared networks, where providers and users interact directly and make further decisions.
In service cryptocurrency development, key considerations to note:
-
Service quality verification and uptime assurance are essential for maintaining user trust.
-
Fair pricing models driven by demand and supply that increase trust in the digital currencies.
-
Reliable incentive mechanisms encourage consistent participation from service providers.
Well-known examples include:
-
Helium rewards users for providing wireless network coverage.
-
Golem, enabling decentralized computing power.
-
Storj supports decentralized cloud storage.
Adoption grows as decentralized services prove reliable alternatives to traditional providers.
Best suited for:
Projects delivering infrastructure services, decentralized marketplaces, or peer-to-peer digital utilities use service cryptocurrencies.
6. Media, Entertainment & Digital Ownership Cryptocurrencies
These cryptocurrencies focus on how content is created, owned, distributed, and monetized in digital environments. Their adoption is driven by creators and users seeking better ownership rights, fair compensation, and direct engagement without centralized platforms.

These currencies gain attention when they give users verifiable ownership, new revenue models, and transparent value exchange.
-
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
NFTs represent unique digital assets stored on the blockchain. Unlike traditional digital files, NFTs allow creators and buyers to verify ownership and authenticity.
Users choose NFTs because they:
-
Prove ownership of digital or physical-linked assets with ease of use.
-
Enable creator royalties that generate ongoing income from secondary sales.
-
Direct creator-to-audience transactions reduce platform dependency and strengthen communities.
The development focuses on these things:
-
Metadata storage and permanence are becoming important to manage perfectly.
-
Marketplace compatibility is necessary, particularly for newly launched NFT platforms.
-
Royalty generation and distribution mechanisms have to be clear, transparent, and fair without any bias.
Prominent examples include:
-
CryptoPunks is one of the earliest NFT collections.
-
Bored Ape Yacht Club, combining digital ownership with community access.
-
NBA Top Shot, bringing licensed sports collectibles to blockchain.
NFT adoption grows when ownership rights deliver value beyond speculation.
Best suited for:
Digital art platforms, collectibles, licensing models, and creator-led NFT marketplaces development can use these cryptocurrencies.
-
Metaverse Cryptocurrencies
Metaverse cryptocurrencies power virtual worlds where users interact, build assets, and trade digital goods. These tokens act as economic layers inside immersive digital environments.
Users adopt metaverse cryptocurrencies because they:
-
Buy virtual land and assets with provable ownership.
-
Participate in digital economies governed by users and not centralized platforms.
-
Monetize creativity, such as virtual experiences or products based on what is famous.
These crypto development priorities include:
-
Scalable virtual asset management is a notable task to manage in an agile way.
-
Interoperability with wallets and marketplaces can improve the utilization of the assets.
-
Stable in-world economies help reduce excessive volatility within virtual platforms.
Well-known examples include:
-
Decentraland (MANA) enables virtual land ownership.
-
The Sandbox (SAND) supports user-created virtual experiences.
-
Axie Infinity ecosystem tokens support virtual economies.
Adoption increases in this cryptocurrency as virtual worlds provide real social and economic value.
Best suited for:
Virtual environments, digital commerce platforms, and interactive entertainment ecosystems use Metaverse cryptocurrencies.
-
GameFi & Play-to-Earn Tokens
GameFi tokens integrate blockchain economics into gaming experiences. Players earn, trade, or upgrade assets through gameplay.
Users choose GameFi tokens because they:
-
Earn real value through participation, not gameplay or entertainment.
-
Own in-game assets, transferable outside the game. This encourages trust in the tokens.
-
Engage in player-driven economies; the community takes forward the token value.
The development considerations include:
-
Balanced reward systems to avoid inflation and maintain trust in the play-to-earn tokens.
-
Smooth onboarding for non-crypto gamers encourages acceptance across the platforms.
-
Long-term sustainability depends on balanced gameplay design and responsible token economics.
Recognized examples include:
-
Axie Infinity combines NFTs with play-to-earn mechanics.
-
Gala Games supports blockchain-based game ecosystems.
-
Immutable X, enabling scalable NFT-based gaming assets.
Adoption for these currencies improves when gameplay quality aligns with sustainable economic incentives.
Best suited for:
Blockchain games, esports platforms, and interactive digital economies can develop these cryptocurrencies.
Choosing the right cryptocurrency for development depends on adoption, utility, and long-term relevance. Projects succeed when they solve real problems, support users naturally, and integrate smoothly into existing ecosystems. Keep prioritizing trends and user preferences by analyzing the news related to cryptocurrencies.
 BTC - Bitcoin
BTC - Bitcoin
 USDTERC20 - USDT ERC20
USDTERC20 - USDT ERC20
 ETH - Ethereum
ETH - Ethereum
 BNB - Binance
BNB - Binance
 BCH - Bitcoin Cash
BCH - Bitcoin Cash
 DOGE - Dogecoin
DOGE - Dogecoin
 TRX - TRON
TRX - TRON
 USDTTRC20 - USD TRC20
USDTTRC20 - USD TRC20
 LTC - LiteCoin
LTC - LiteCoin